GitHub
This guide walks you through preparing your GitHub environment for MCPMark and authenticating the CLI tools with support for token pooling to mitigate rate limits.
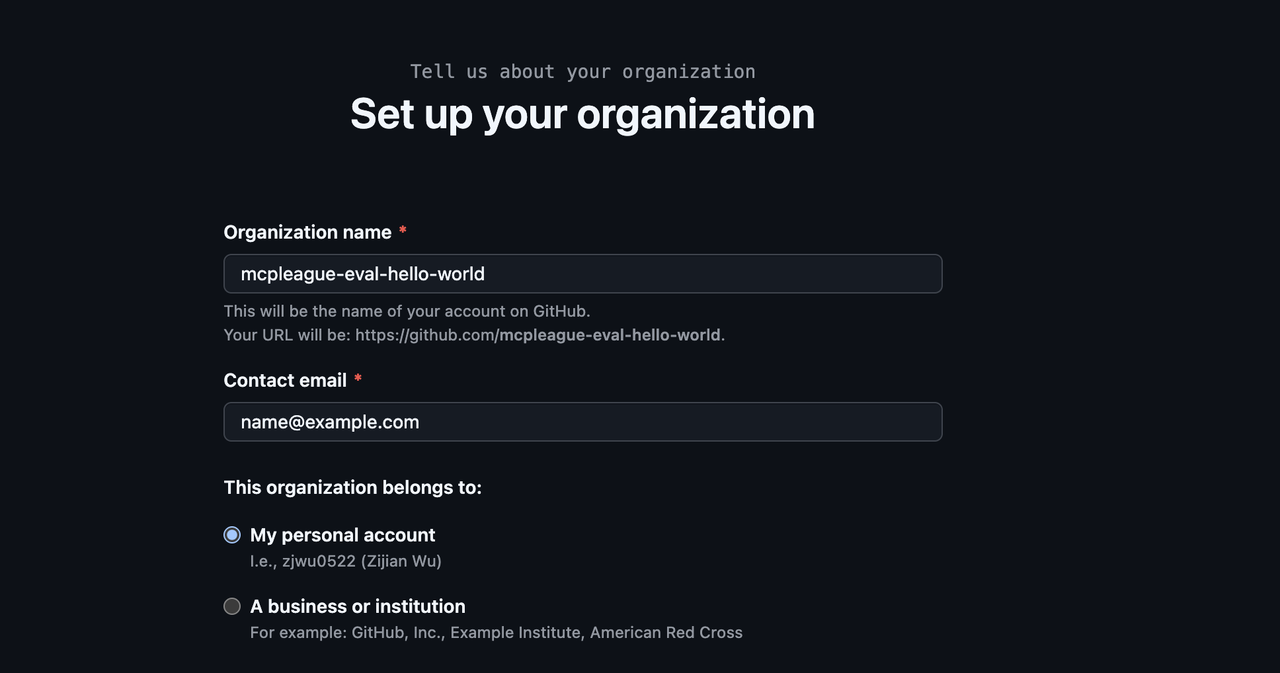
1 · Prepare An Evaluation Organization in Github
-
Create a free GitHub Organization
-
Create Multiple GitHub Accounts (Recommended for Rate Limit Relief)
To effectively distribute API load and avoid rate limiting, we recommend creating 2-4 additional GitHub accounts:- Create new GitHub accounts (e.g.,
your-name-eval-1,your-name-eval-2, etc.) - Important: Add all these accounts as Owners to your evaluation organization
- This allows the token pooling system to distribute requests across multiple accounts
- Create new GitHub accounts (e.g.,
-
Generate Fine-Grained Personal Access Tokens (PATs) for Each Account
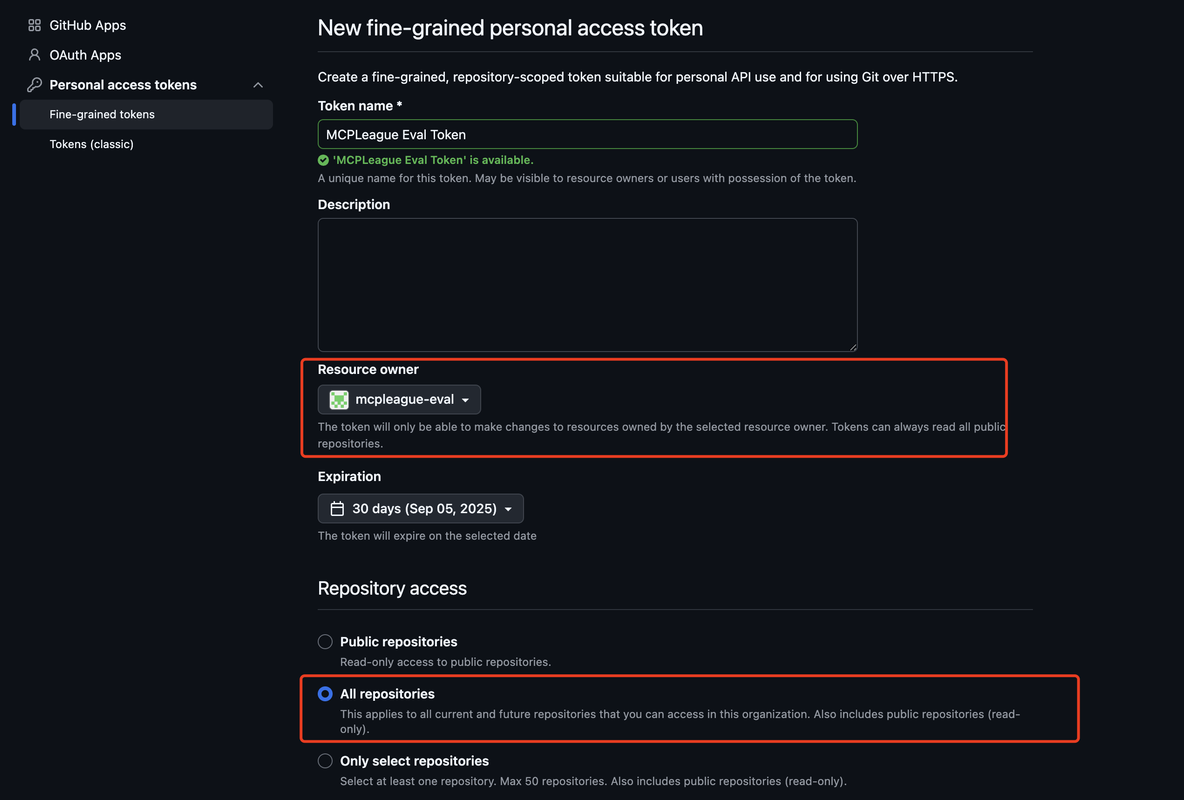
Repeat the following process for each GitHub account (including your main account):- Navigate to Settings → Developer settings → Personal access tokens → Fine-grained tokens
- Click Generate new token, select the evaluation organization you created
- Give the token a descriptive name (e.g., MCPMark Eval Token - Account 1)
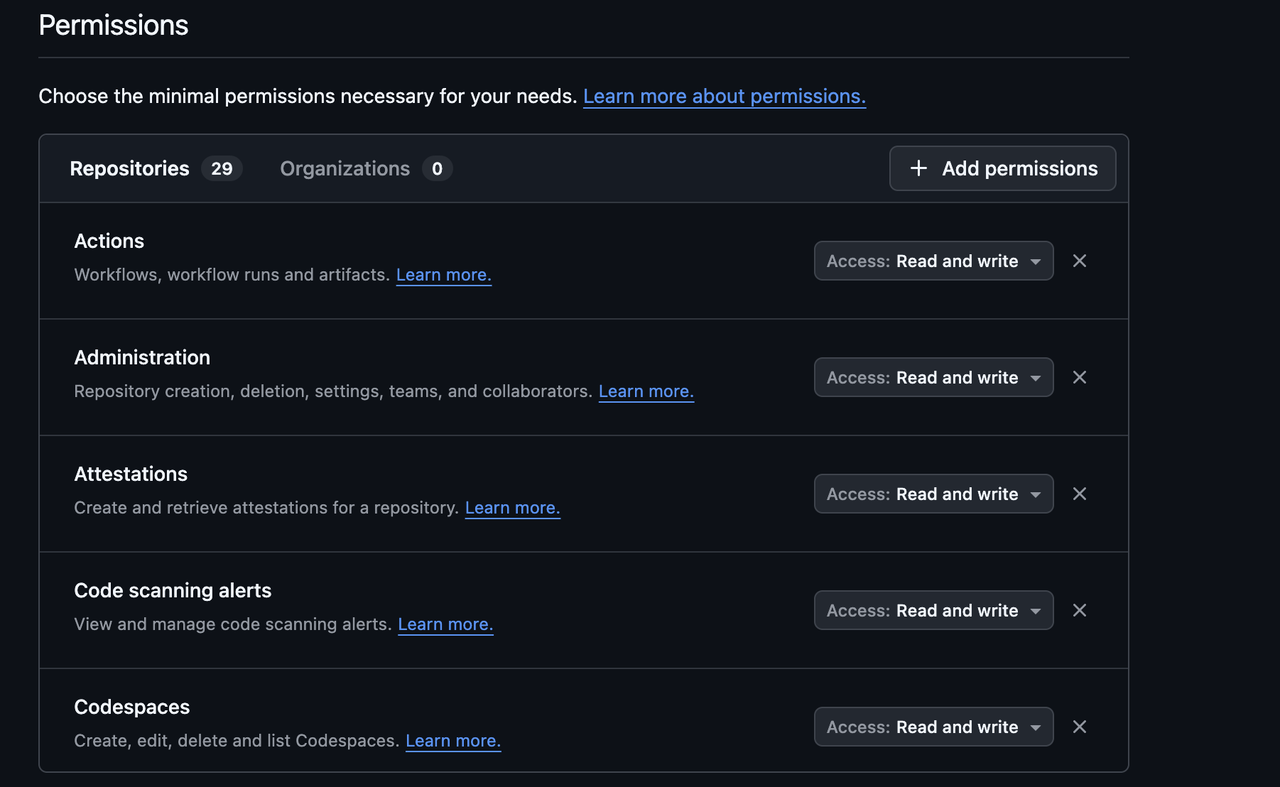
- Under Repository permissions and Organization permissions, enable All permissions (read and write if applicable)
- Copy the generated token and save it safely — you'll need all tokens for the next step
-
Configure Token Pooling in
.mcp_env
In your project root, edit (or create) the.mcp_envfile and add your tokens:For single token (Basic setup):
PlaintextFor multiple tokens (Recommended for handling rate limits):
PlaintextImportant Notes:
- Replace
token1,token2,token3,token4with your actual tokens (comma-separated, no spaces) - 2-4 tokens is recommended for optimal rate limit distribution
- All tokens must have the same permissions on the evaluation organization
- The system automatically rotates between tokens to distribute API load
- Replace
2 · Download the Sample Repository State
We have pre-exported several popular open-source repositories along with curated Issues and PRs.
-
Download the archive from Google Drive.
-
Extract it so that the directory
./github_state/appears in the project root:Shell
3 · Add New Repositories (Optional)
If you want to benchmark additional repositories:
- Export the desired repository state:
Shell
- Open
src/mcp_services/github/state_manager.pyand add a new entry toself.initial_state_mappingpointing to the exported folder.
4 · GitHub Rate Limits & Token Pooling Benefits
Understanding Rate Limits
Fine-grained tokens are subject to GitHub API rate limits:
- Read operations: 5,000 requests per hour per token
- General write operations: 80 writes per minute and 500 writes per hour per token
- Content creation (Issues, PRs, Comments): 500 requests per hour per token (Secondary Rate Limit)
How Token Pooling Helps
With token pooling, MCPMark automatically:
- Distributes requests across multiple tokens to multiply your rate limits
- Rotates tokens for each task execution to balance load
- Handles rate limit failures by trying the next available token
- Ensures consistency between agent execution and verification
Example: Rate Limit Multiplication
Read Operations:
- Single token: 5,000 requests/hour
- 4 tokens: ~20,000 requests/hour total capacity
Content Creation (Critical for MCPMark):
- Single token: 500 content creation requests/hour
- 4 tokens: ~2,000 content creation requests/hour total capacity
- Automatic failover: If one token hits limits, others continue working
This dramatically improves evaluation performance, especially for large task batches or frequent testing cycles. The content creation limit is often the bottleneck, making token pooling essential for efficient evaluations.
Repository Limits
MCPMark places a cap on the number of PRs and issues (≤ 50 in total) per repository to ensure reasonable evaluation times and to stay within rate limits.
2. Running Github Tasks
-
Configure environment variables: make sure
GITHUB_TOKENSandGITHUB_EVAL_ORGare properly set in.mcp_env. -
For single task or task group, run
Here EXPNAME refers to customized experiment name, GITHUBTASK refers to the github task or task group selected (see Task Page for specific task information), MODEL refers to the selected model (see Introduction Page for model supported), K refers to the time of independent experiments.